A Temporal Fusion Transformer was trained with Adaptive downsampling using RDP downsampling, in a notebook in ~/cernbox/hysteresis/dipole/notebook/adaptive-downsampling/train-tft.ipynb, then exported to a python file to run with DDP on 3 gpus on ml003.
Hyperparameters
The hyperparameters used were:
PAST_KNOWN_COVARIATES = ["B_sim_T_A"]
KNOWN_COVARIATES = ["I_sim_A", "I_sim_A_dot"]
TARGET_COVARIATE = "B_sim_T"
TARGET_DEPENDS_ON = "I_sim_A"
TIME = "time_ms"
CTXT_SEQ_LEN = 800
TGT_SEQ_LEN = 200
MIN_CTX_SEQ_LEN = 200
MIN_TGT_SEQ_LEN = 200
BATCH_SIZE = 64
N_DIM_MODEL = 300
HIDDEN_CONTINUOUS_DIM = 100
NUM_HEADS = 4
NUM_LSTM_LAYERS = 2
DROPOUT = 0.1
LR = 1e-3Adding time as a feature
And an additional feature was added to the known_covariates. After all covariates were transformed / normalized, RDP was applied with to the I_sim_A, time_ms and B_sim_T columns in the training and validation set to generate a mask that was applied to the training and validation dataframes. The be reduced in steps of for more points.
For sample generation, the __getitem__ was monkey-patched using
def __getitem__(self, idx: int) -> EncoderDecoderTargetSample:
sample = EncoderDecoderDataset.__getitem__(self, idx)
feature_idx = len(KNOWN_COVARIATES)
sample["encoder_input"][0,...,feature_idx] = 0.0
# sample["decoder_input"][0,...,feature_idx] = 0.0
return sample
train_dataset.__getitem__ = types.MethodType(__getitem__, train_dataset)
valid_dataset.__getitem__ = types.MethodType(__getitem__, valid_dataset)to make the first for the encoder input, but leave it nonzero for the decoder input, to retain continuity between the encoder and decoder sequences.
Training performance
Without adaptive downsampling with the full 1kHz signal with 4 hours of data took 4-5 hours per epoch to train. With RDP and , we retain 2.13 % of all points, equivalent to a downsampling by 46. Using a torch compiled model with the same hyperperameters as before, each epoch now takes 3m45s.
Additional data was added (24h equivalent) with an adapted , and adjusted CTXT_SEQ_LEN=600, each epoch takes 22 minutes
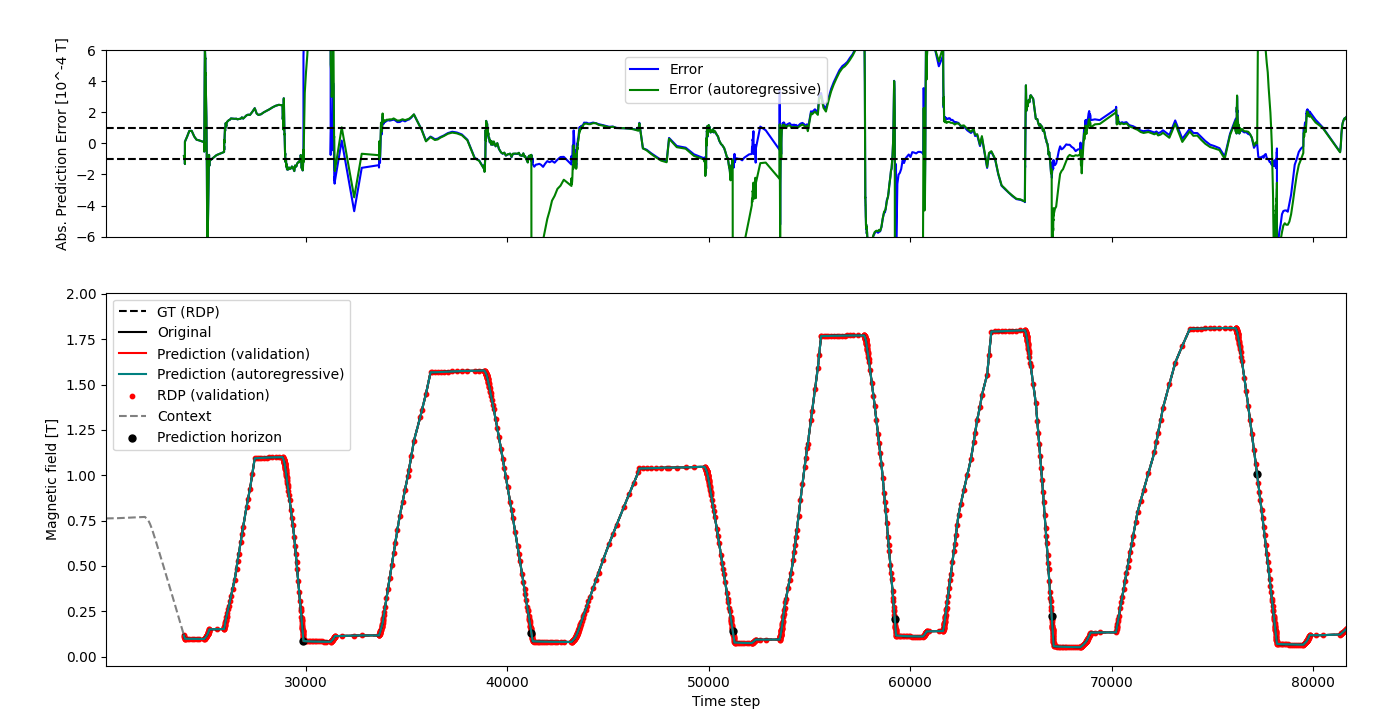
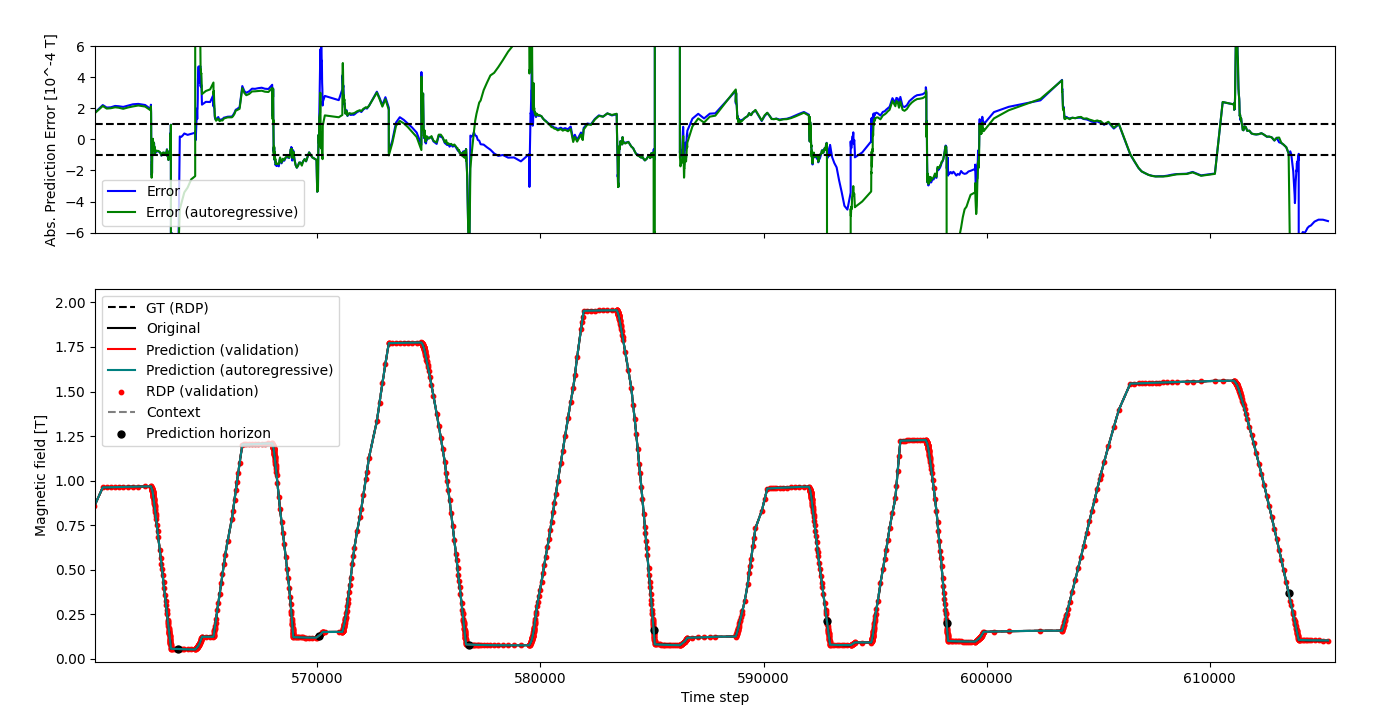
Validation and autoregressive predictions
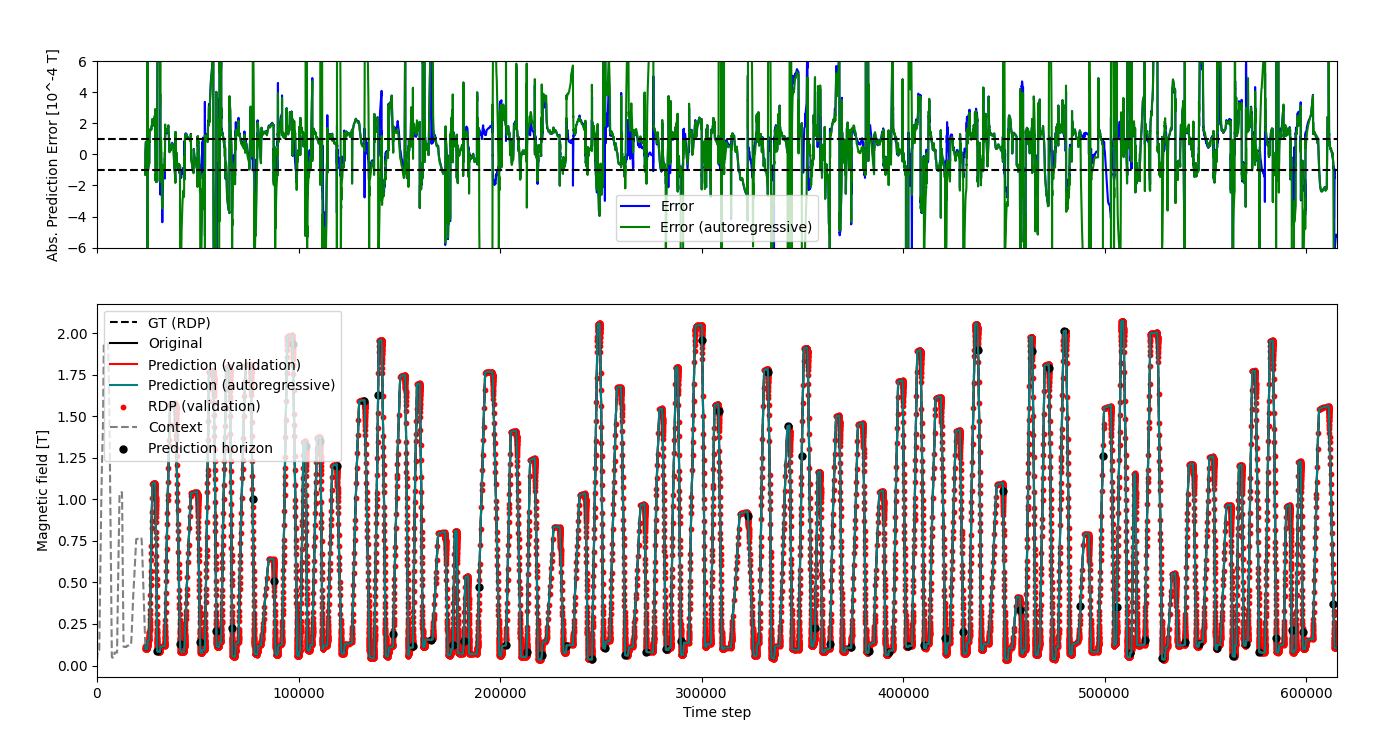
At the beginning
and at the end. The autoregressive prediction does not seem to diverge too much.
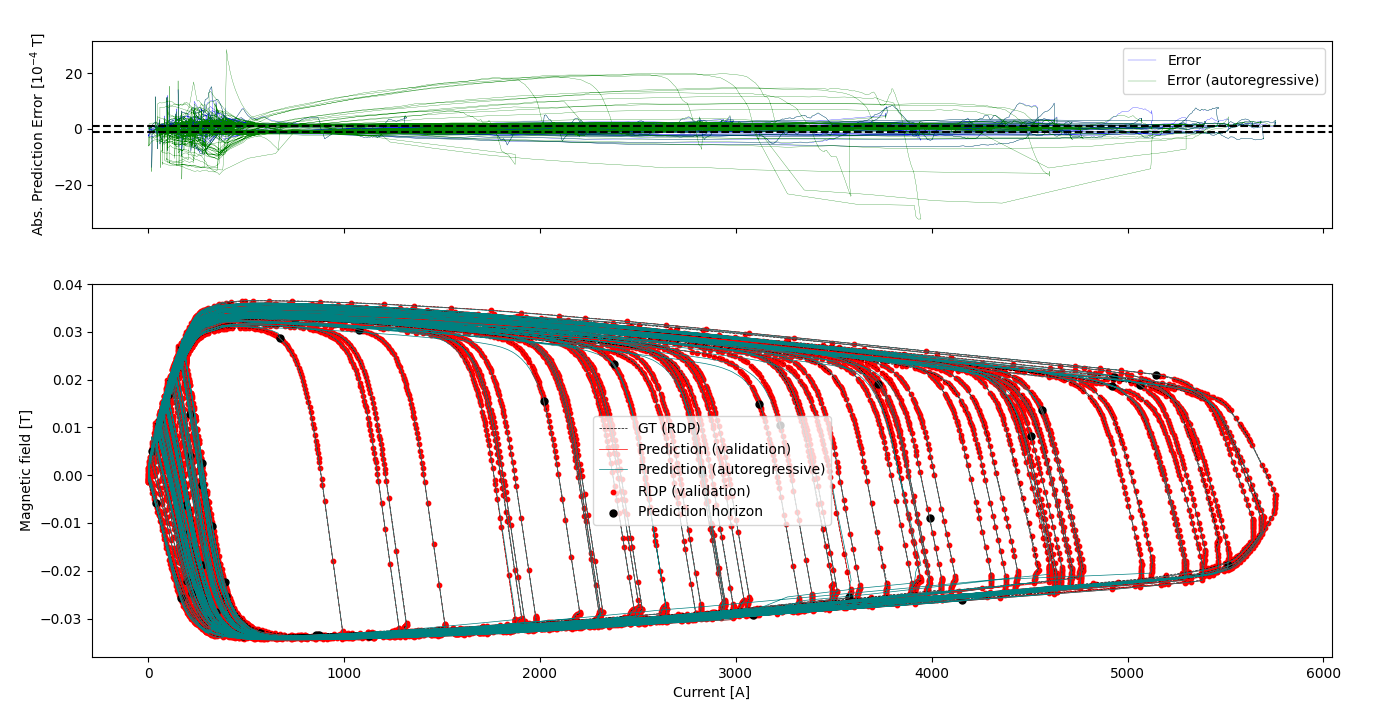
Validation error: mean=0.3540, std=2.1545, max=15.2152, max_90=2.3364
Autoregres error: mean=0.3398, std=4.3847, max=28.5958, max_90=3.9522
Validation RMSE: 0.0002, SMAPE: 0.0871
Autoregres RMSE: 0.0004, SMAPE: 0.1426
In T, we can clearly see a larger variance in the autoregressive prediction, with a twice higher max prediction error at roughly 10% of the original domain. This is seen as well on the RMSE and SMAPE scores.
This does suggest the autoregressive prediction to be less reliable.
In general we see significantly worse performance on the flat bottom, a.k.a. the remanent field.
Potential improvements
We could use a few different as a method of data augmentation to provide more variation of points along the curves, to generalize the model better with variable number of points, which is the case for inference.