Combining lowpass filters, low amplitude noise filters and adaptive downsampling, we can effectively reduce the dimensionality of the measured time series data without losing too much information.
Prior to applying RDP, the current and field needs to be normalized with standard scaling, since current and fields have different magnitudes. Additionally the time axis is defined in seconds, instead of milliseconds. Setting the threshold to empirically, we get
rdp_mask = rdp(
np.column_stack(
(
(train_df["time_ms"].to_numpy() - train_df["time_ms"].to_numpy()[0]) / 1e3,
current_scaler.transform(current),
field_scaler.transform(field - calibration_fn(current).numpy()),
)
),
# epsilon=2e-5,
epsilon=6.5e-4,
return_mask=True
).astype(bool)And we retain 328091 / 3273600 - 10.02% points, effectively equivalent to a factor 10 downsampling.
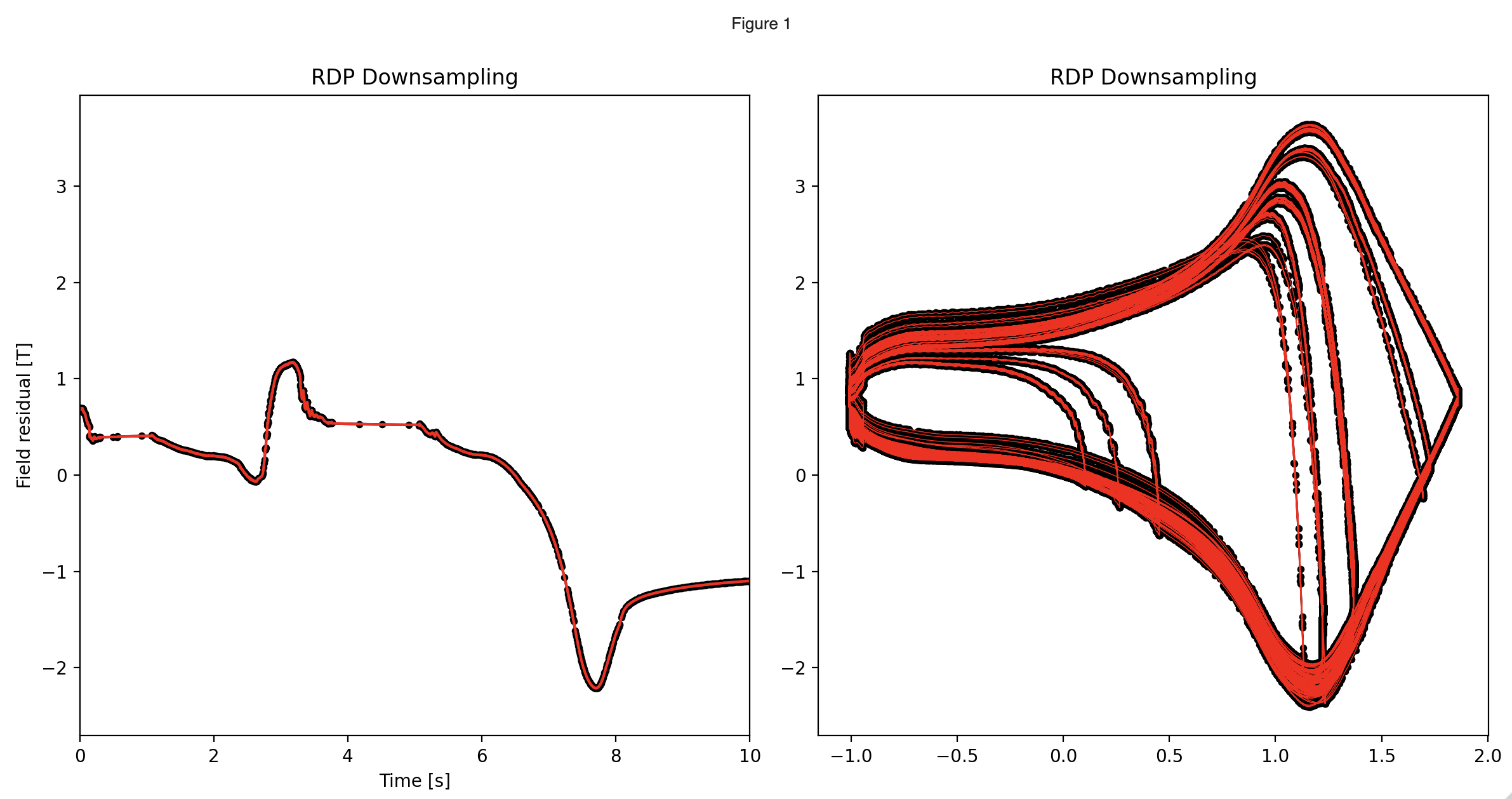
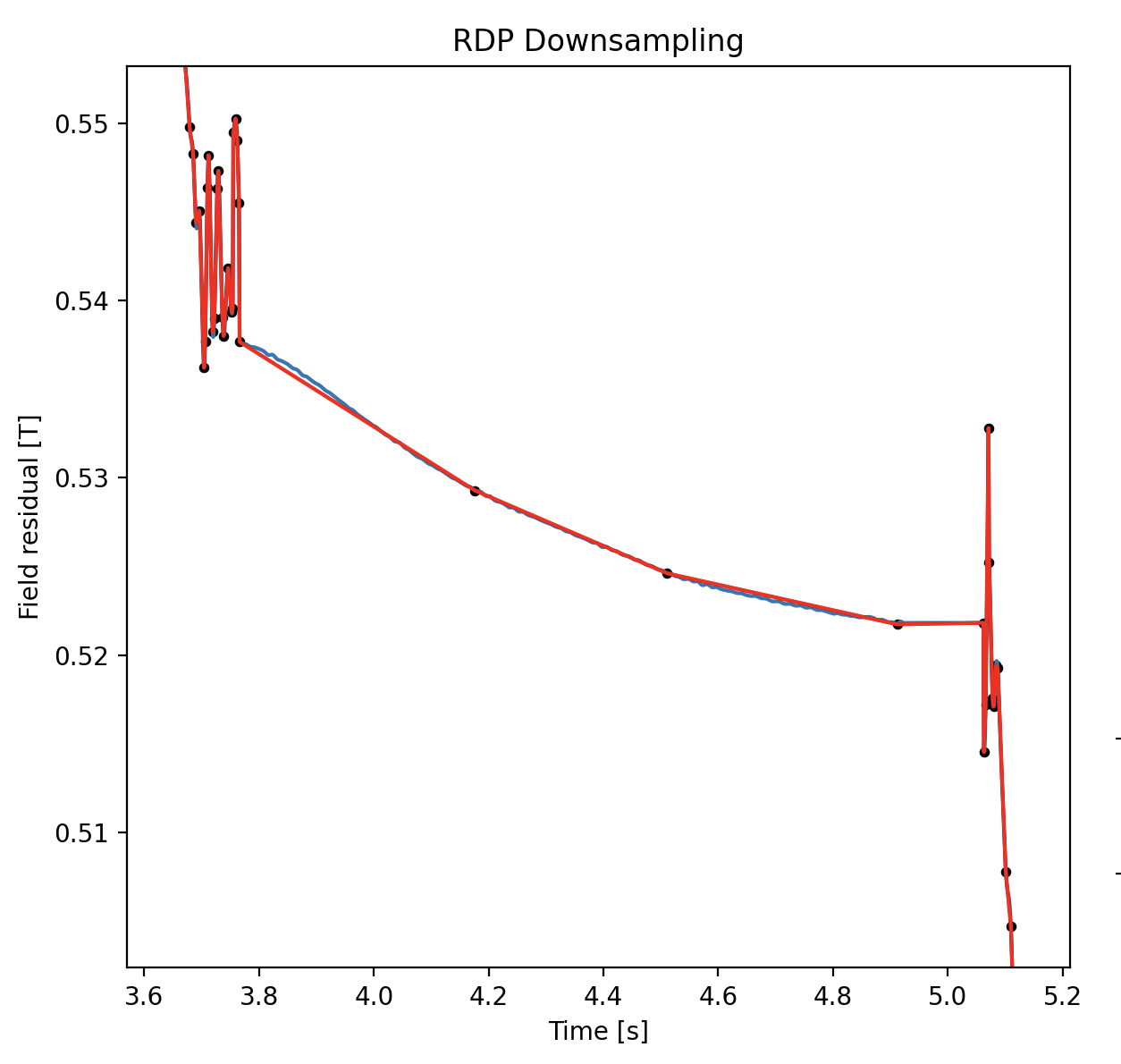 The downsampled data effectively captures the fast and slow changes in the signal, showing the eddy current decay, while still showing medium frequency waves from the original signal:
The downsampled data effectively captures the fast and slow changes in the signal, showing the eddy current decay, while still showing medium frequency waves from the original signal:
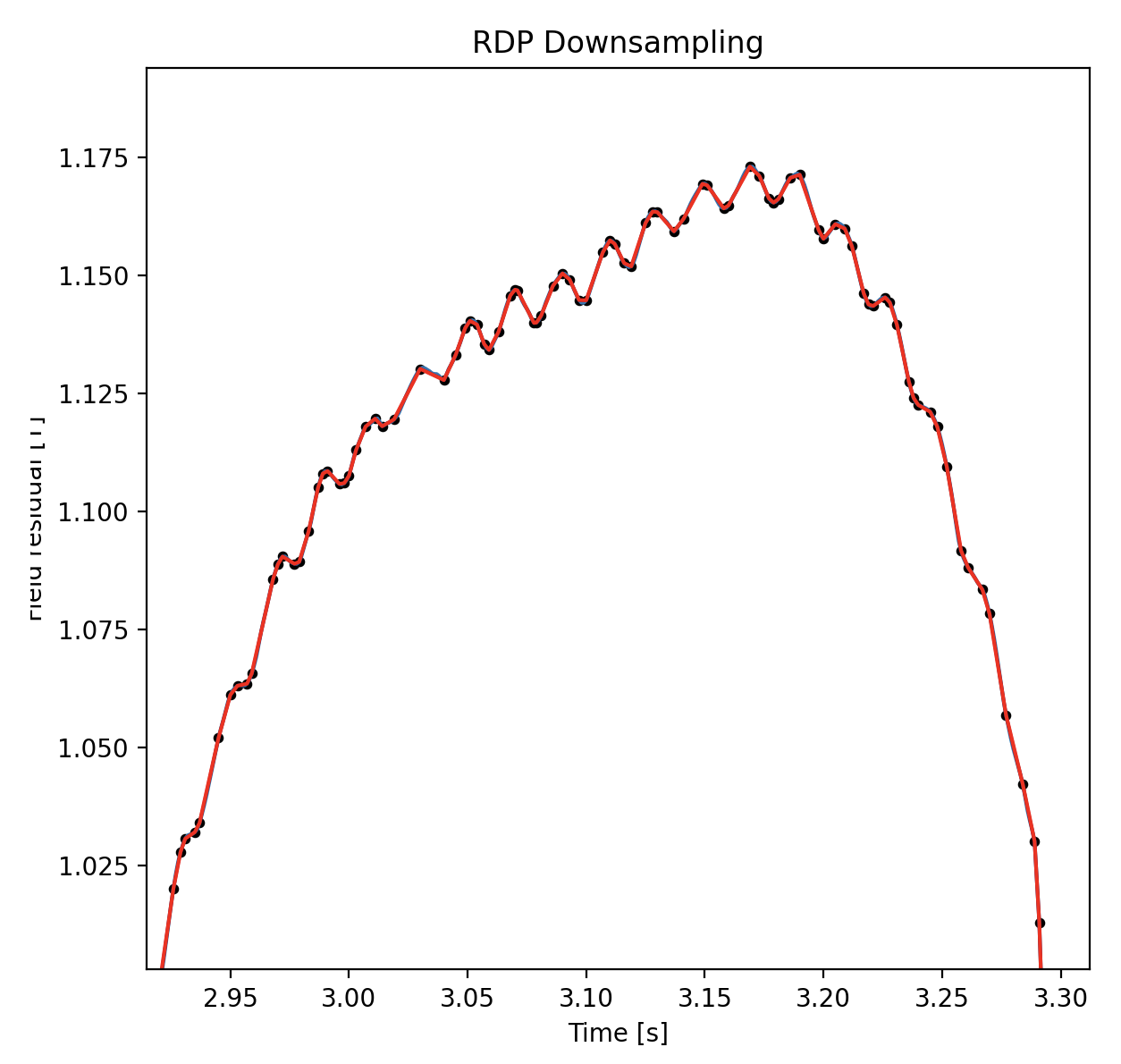 We can then use this reduced dataset to do transfer learning using Temporal Fusion Transformer with adaptive downsampling.
We can then use this reduced dataset to do transfer learning using Temporal Fusion Transformer with adaptive downsampling.