Implemented in ~/cernbox/hysteresis/dipole/notebooks/low-amplitude-filter/low-amplitude-filter.ipynb
Low amplitude noise can be found in both the measured current and field from the SPS MBIs. This makes it challenging to downsample the time series while retaining information and discarding noise. This is especially true for the injection plateaus of the SPS cycles, where extremely small variations in field ( T) are measurable on the beam.
While certain phenomenon like power supply ripples are translated from current to field, they cannot be compensated for, since this is a constraint in the physical system. Hence we would prefer to not model them, and we can remove them from data without significant loss of information.
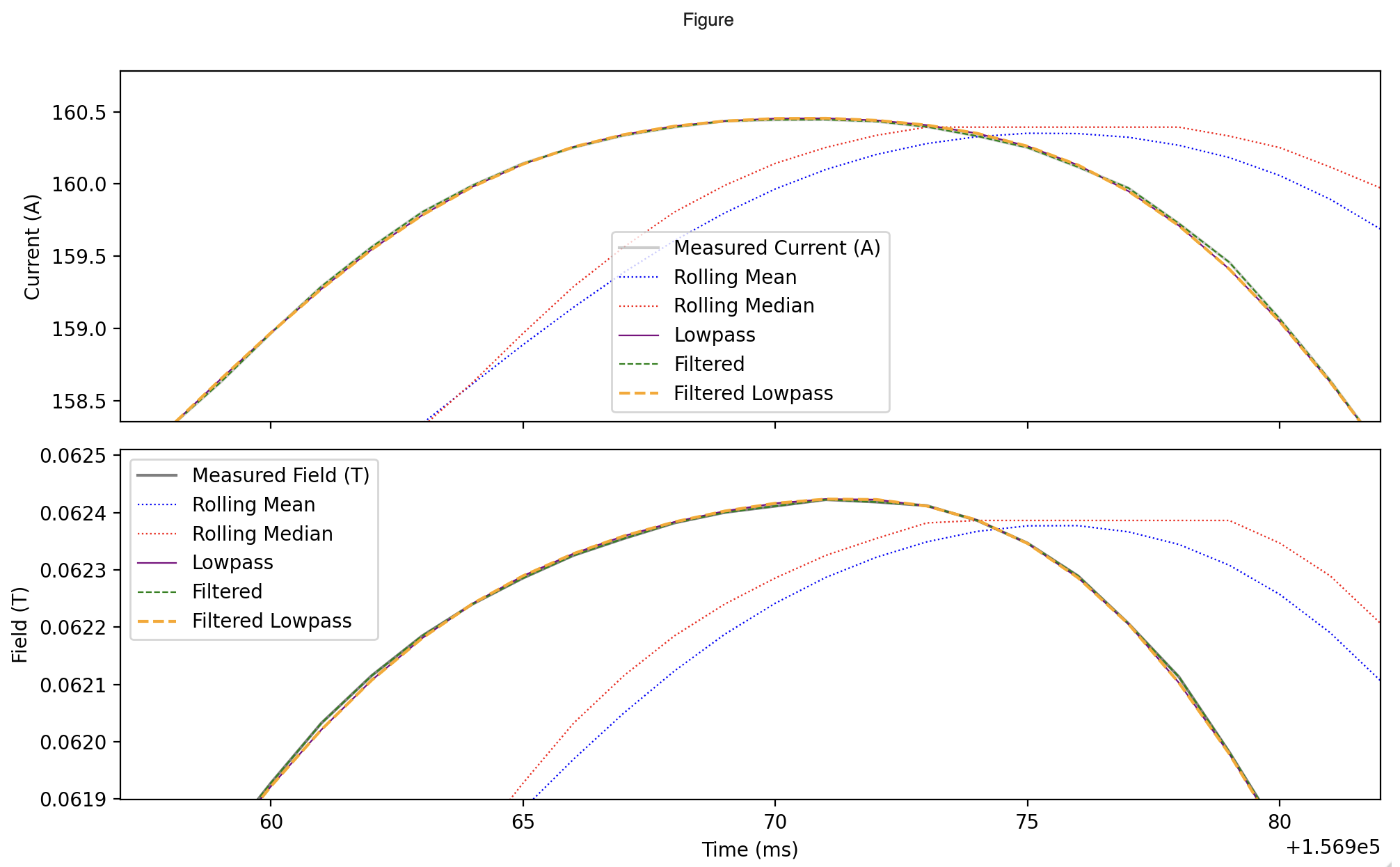
Below we can see a comparison between the measured current and field, and their respective rolling mean, median, lowpass filtered, low amplitude filtered, and lowpass + low amplitude filtered, using the following parameters:
i_rolling_mean = i_meas.rolling(window=11).mean()
i_rolling_median = i_meas.rolling(window=11).median()
i_lowpass = butter_lowpass_filter(i_meas, 90, 1e3, 3)
b_rolling_mean = b_meas.rolling(window=11).mean()
b_rolling_median = b_meas.rolling(window=11).median()
b_lowpass = butter_lowpass_filter(b_meas, 90, 1e3, 3)
i_filtered = low_amplitude_filter(i_meas, window_size=101, threshold=0.06 / 2)
b_filtered = low_amplitude_filter(b_meas, window_size=101, threshold=1.5e-5 / 2)
i_filtered_lp = low_amplitude_filter(i_lowpass, window_size=151, threshold=0.06 / 2)
b_filtered_lp = low_amplitude_filter(b_lowpass, window_size=151, threshold=1.5e-5 / 2)The lowpass filter cutoff frequency and order are selected empirically. The lower the cutoff frequency, the more high frequency noise is removed, but more information is lost, especially where the rate of change is high.
The low amplitude filtered thresholds are selected from data. The noise and ripples in the measured current are in A, and T, and additional slack is added for safety.
SFTPRO1 flat bottom
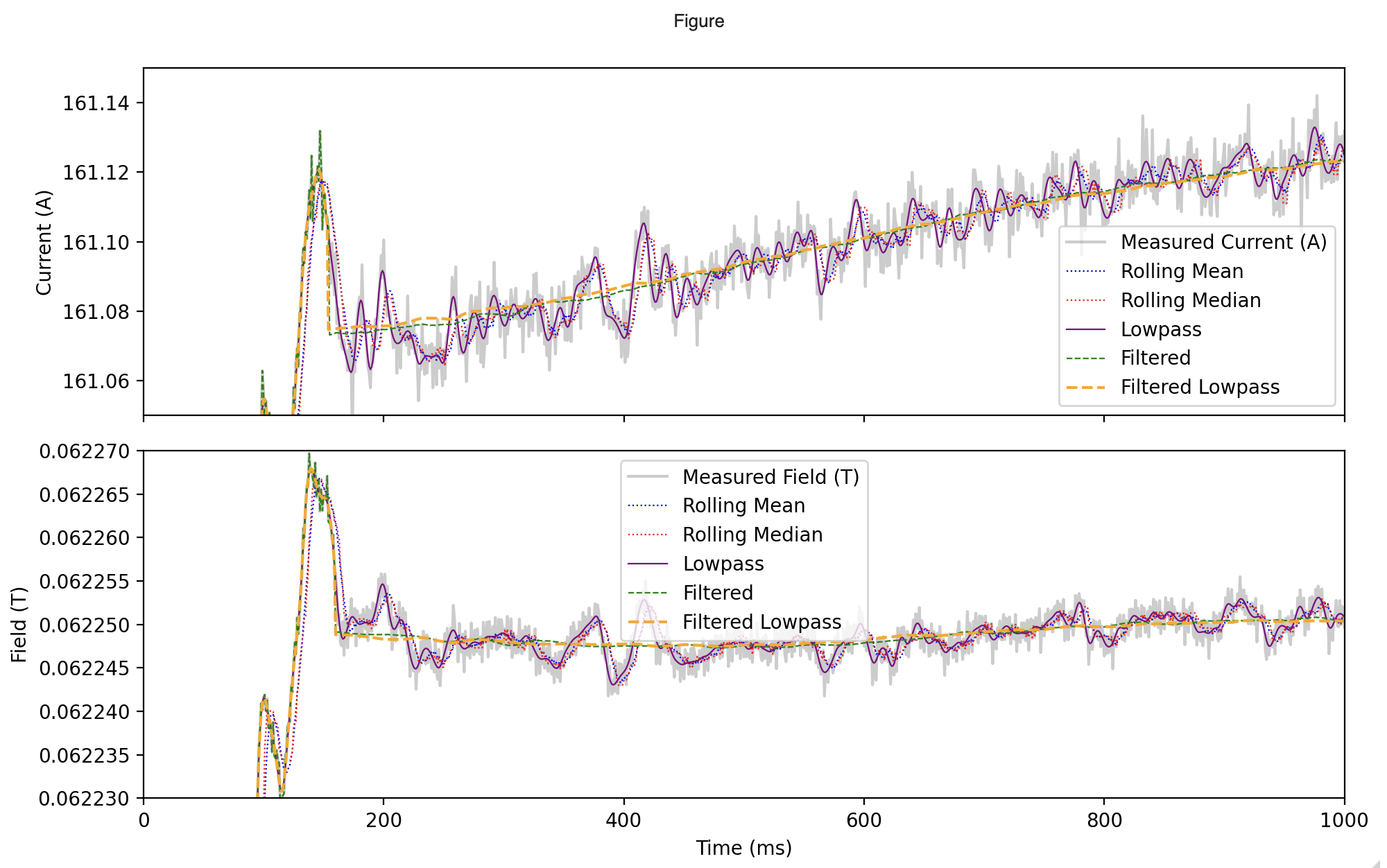 The dotted lines (rolling mean and median) can be seen lagging behind the real signal. This is inherent to the smoothing methods.
The dotted lines (rolling mean and median) can be seen lagging behind the real signal. This is inherent to the smoothing methods.
The low amplitude filtered signal (green dashed) follow the real signal well, but is very sensitive to the choice of threshold, and still intentionally leaves out noise at where amplitudes are above the threshold, this is especially seen at the injection plateau.
The lowpass filtered signal (purple solid) follow the real signal very well, but does not smooth out oscillations where the frequency is high. However applying a low cutoff frequency will degrade signal where there are high amplitude, high frequency oscillations, like at the ramp down.
We can instead employ a combination, using a lowpass filter with a high cutoff frequency to get rid of high-frequency noise, and then a low amplitude noise filter after it, to remove the lower amplitude, medium amplitude oscillations.
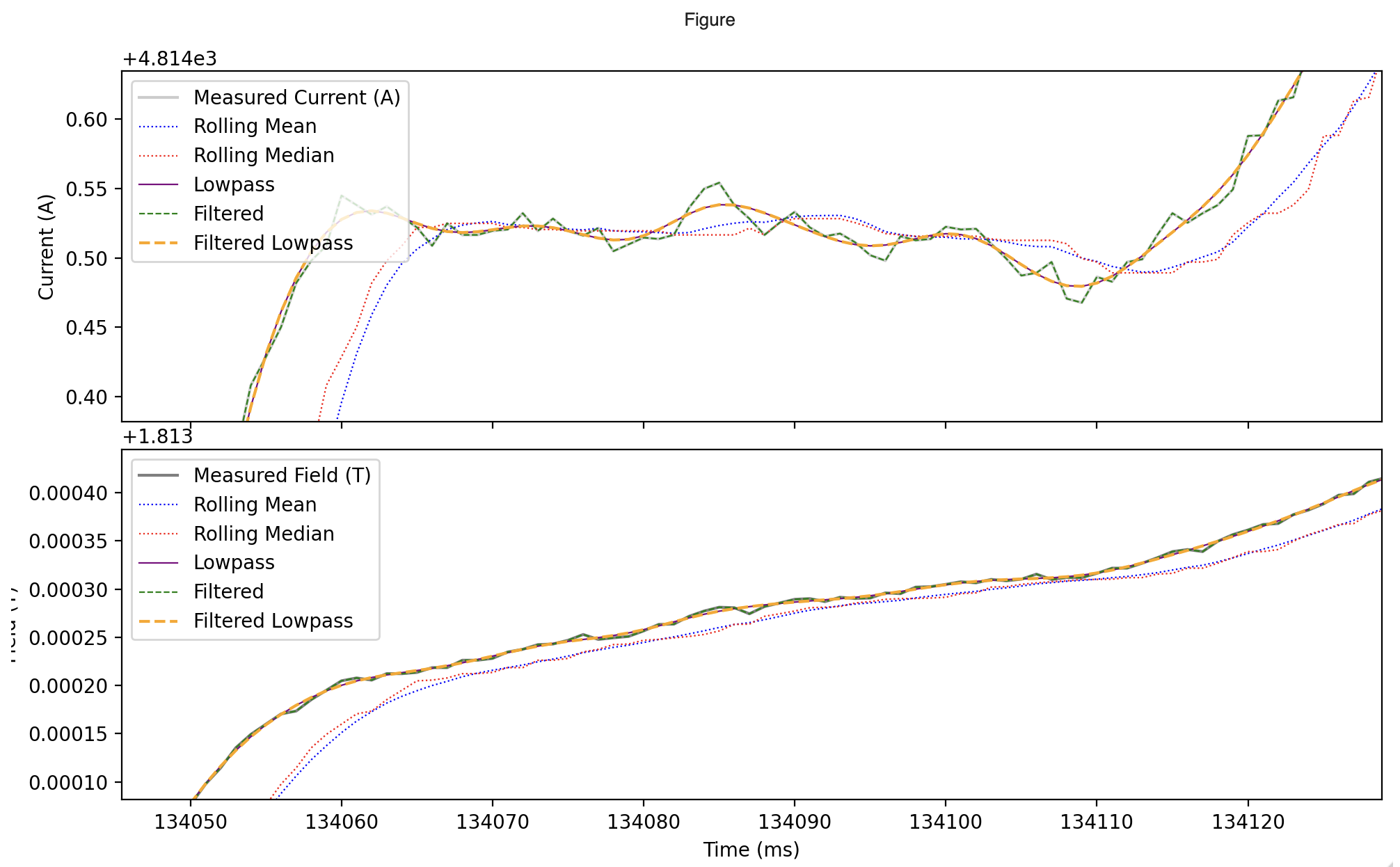
SFTPRO1 flat top beginning
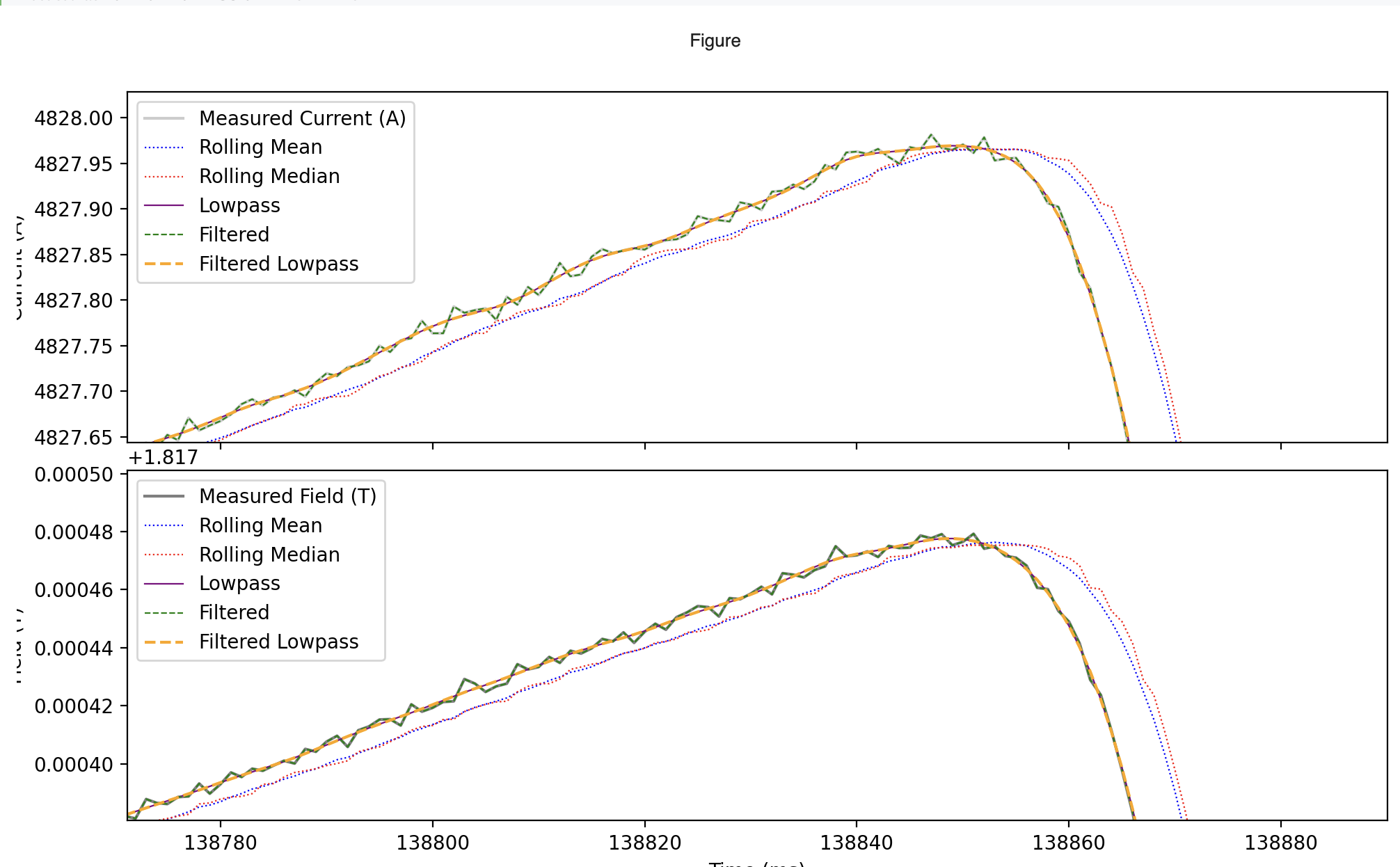
SFTPRO1 flat top end
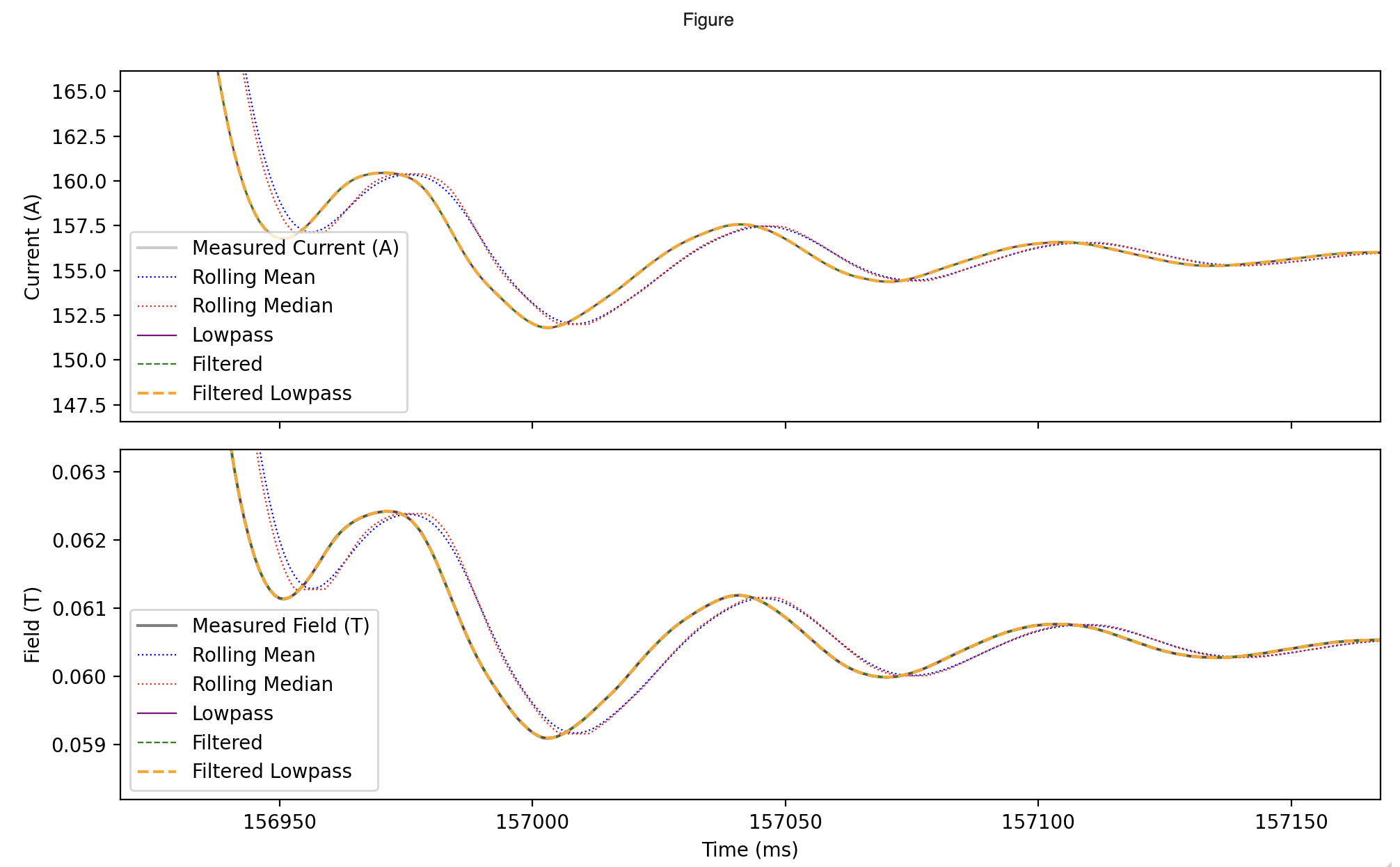
SFTPRO1 ramp down ripples
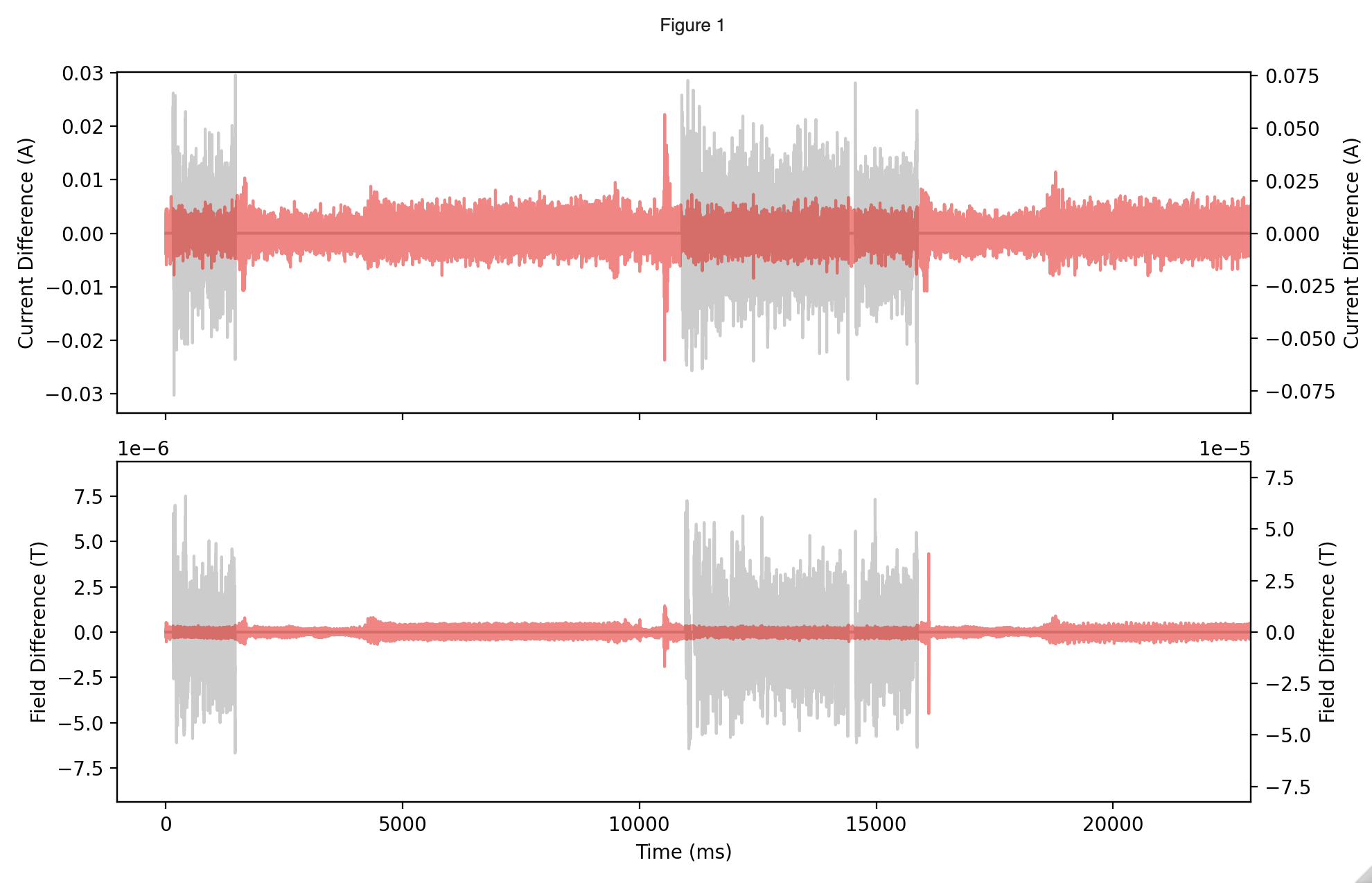
Investigating how much a lowpass filter (red) and a low amplitude filter (gray) removes noise from signal.
For the measured current, the low amplitude filter removes signal up to A, and A using the lowpass filter. Similarly, the low amplitude filter removes T for the measured field, and T using a lowpass filter.
 Further, the difference between between lowpass filtered and lowpass + low amplitude filtered data is
Further, the difference between between lowpass filtered and lowpass + low amplitude filtered data is
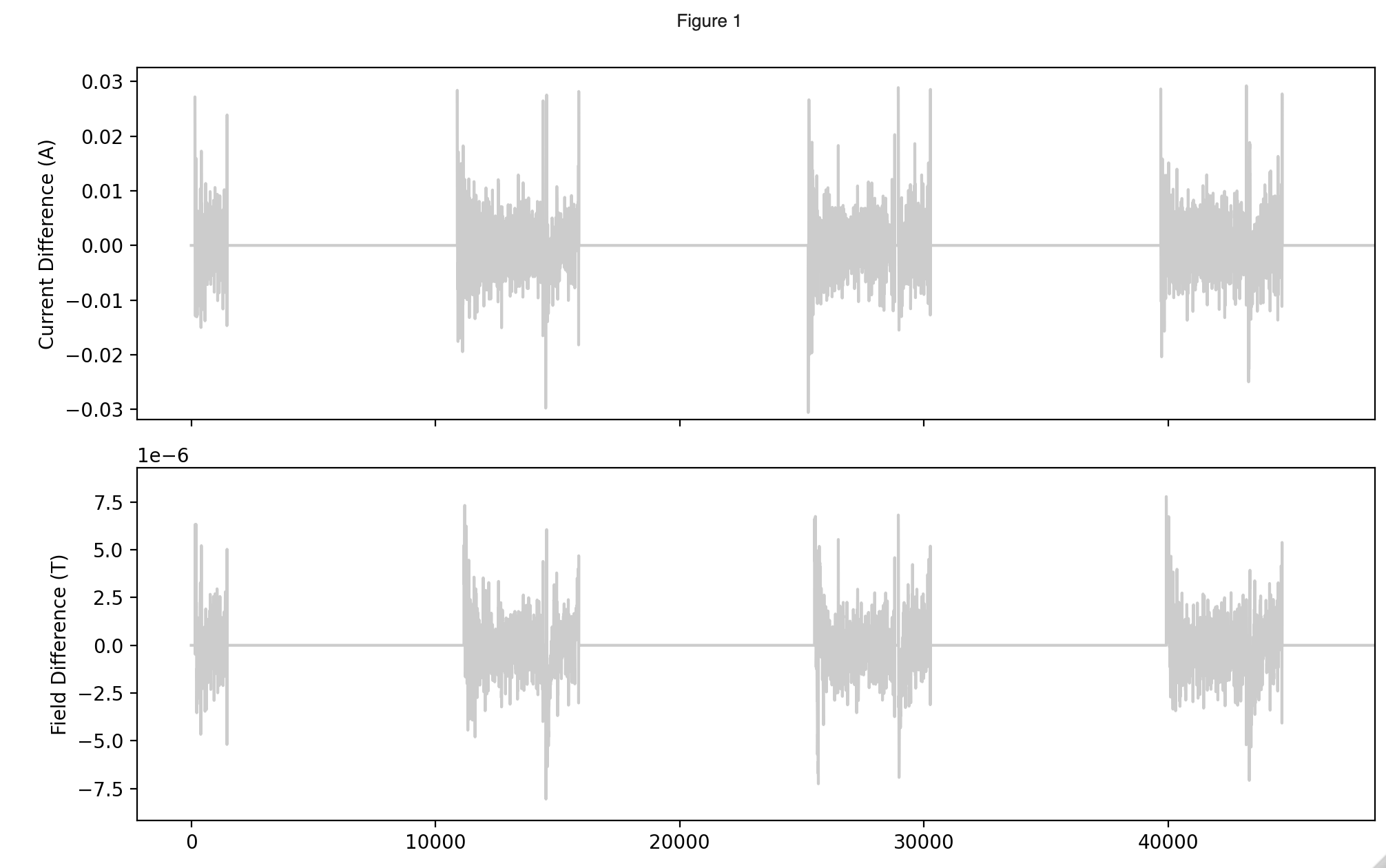 We can clearly see the low amplitude noise removed in the domains A and T. If we want to be accurate in , we must remove the low amplitude noise. Most importantly, the noise is only removed on the plateaus, where the noise is most pronounced.
We can clearly see the low amplitude noise removed in the domains A and T. If we want to be accurate in , we must remove the low amplitude noise. Most importantly, the noise is only removed on the plateaus, where the noise is most pronounced.
Following removing the noise we can more easily perform Adaptive downsampling with RDP.
Filter by cycle
It is simple to perform the lowpass and low amplitude filtering on entire time series, which is useful during training and validation. However during inference, we predict cycle by cycle. Then it is crucial to perform the filtering by cycle for training data, so it is representative for unseen data.
However this is challenging as the cycle-by-cycle filtering need to be edge-preserving, to avoid discontinuities between cycles.